
Resources and Learning
Learn more about TLS/SSL certificates.

What is an SSL certificate?
An SSL certificate is a code package attached to your web server that provides security for online communications. When a web browser contacts your secured website, the SSL certificate enables an encrypted connection.
SSL certificates also inspire trust because each SSL certificate contains identification information. When you request an SSL certificate, a third party, like Thawte and DigiCert, verifies your organization’s information and issues a unique certificate to you with that information. This is known as the authentication process.
SSL is the common term for this form of web security, but today, these certificates are TLS, a more advanced and secure form of SSL. TLS, TLS/SSL, and SSL are often used interchangeably, but all refer to advanced TLS web security certificates.
How do TLS/SSL certificates work?
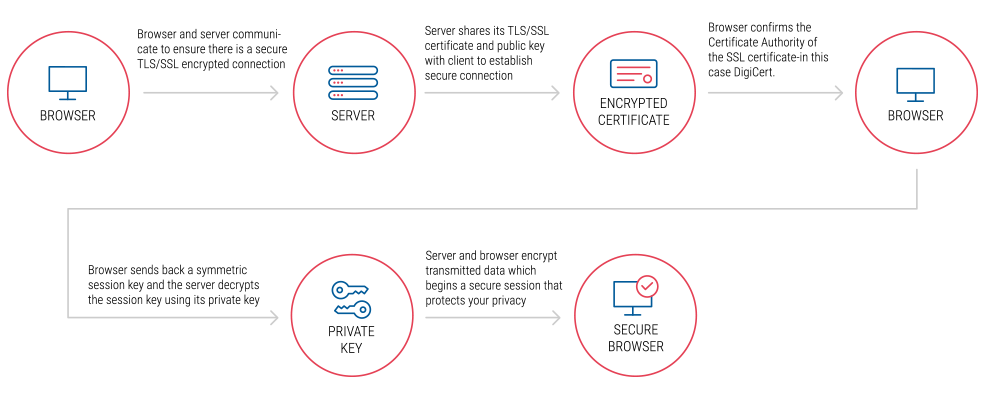
When an Internet user visits a secure web site, an SSL certificate provides identification information about the web server and establishes an encrypted connection. This process happens in a fraction of a second.
What happens between the web browser and server:
- A browser attempts to connect to a web site secured with SSL. The browser requests that the web server identify itself.
- The server sends the browser a copy of its SSL certificate.
- The browser checks whether it trusts the SSL certificate. If so, it sends a message to the server.
- The server sends back a digitally signed acknowledgement to start an SSL encrypted session.
- Encrypted data is shared between the browser and the server.
TLS/SSL Fundamentals
There are 3 essential elements at work in the process described above: a protocol for communications (SSL), credentials for establishing identity (the SSL certificate), and a third party that vouches for the credentials (the Certificate Authority).

What happens after I place my certificate order?
Because TLS/SSL operates on identity verification, your certificate is issued when your domain validity is established. Our quick guide explains how validation works.

What is a Certificate Authority?
A TLS/SSL certificate serves as a credential in the online world. Each SSL certificate uniquely identifies a specific domain (like thawte.com) and a web server. Trust of a credential depends on confidence in the organization that issued it.
A Certificate Authority is a third-party, unaffiliated organization that uses different validation methods to establish a real-world connection between a domain and the entity who says they own and manage it. An entity can be an individual, a small business, an enterprise, an organization, or even a government. No matter the size of the entity, a CA certifies trust so website visitors know they’re on the authentic site of that entity and not an imposter.
What is Certificate Lifecycle Management?
Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) is the process of ensuring digital trust by maintaining up-to-date certificates on websites, code, email, documents, servers, and other forms of digital information and communication. When certificates expire, or they’re incorrectly issued or managed, this digital information is vulnerable to attack. In today’s hyper-connected world, unsecured information not only puts organizations at risk, it also represents a threat to site visitors, customers, and any entity that communicates with that data. Healthy Certificate Lifecycle Management eliminates this risk.
Today, smart certificate management platforms and tools make healthy CLM easy with simple-to-use issuance controls and automation, so any needed action can be quickly addressed with minimal effort before something turns into a security risk.
Thawte and DigiCert provide strong and easy Certificate Lifecycle Management for TLS/SSL certificates through DigiCert CertCentral. DigiCert also offers Certificate Lifecycle Management for enterprise IT and IAM, code and software, DNS, documents and signing, and IoT.
Looking for something more?

Why choose Thawte powered by DigiCert?
Thawte is a globally-recognized provider of TLS/SSL certificates—now powered by DigiCert, the industry-leader in high-assurance website security. Our engineers work behind the scenes to ensure both your brand and your customers’ most sensitive personal information are protected. We provide affordable and flexible TLS/SSL certificates to a wide variety of businesses and organizations to reliably secure websites, servers and digital environments. Thawte customers also have access to DigiCert’s award-winning customer support available around the globe.